by Inge Heinzl, Editor, and Marisabel Caballero, Global Technical Manager Poultry, EW Nutrition
What is your most crucial key feed performance indicator? We posted this question on an online professional platform and got more than 330 answers from professionals in the industry:
- 55 % of the respondents considered feed efficiency or feed conversion rate (FCR) the key indicator, and
- 35 % listed feed cost / kg produced as their most important indicator.

As feed represents 60-70 % of the total production costs, feed efficiency has a high impact on farm profitability – especially in times of high feed prices. Furthermore, for the meat industry, an optimal FCR is essential for competitiveness against other protein sources. Finally, for food economists, feed efficiency is connected to the optimal use of natural resources (Patience et al., 2015).
In this article, we explain the factors that influence feed efficiency and show options to support animals in optimally utilizing the feed – directly improving the profitability of your operation.
How to measure the feed conversion rate
The FCR shows how efficiently animals utilize their diet for maintenance and net production. In the case of fattening animals, it is meat production; for dairy cows, it is milk, and for layers, it is egg mass (kg) or a specific egg quantity.
The feed conversion rate is the mathematical relation obtained by dividing the amount of feed the animal consumed by the production it provided. The FCR is an index for the degree of feed utilization and shows the amount of feed needed by the animal to produce one kg of meat or egg mass, or, e.g., 10 eggs.
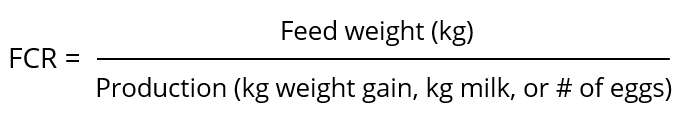
When comparing the FCRs of different groups of animals (e.g., from different houses or farms), some considerations are important:
- Feed consumed is not feed disappeared: Due to differences in feeder design and feeder adjustment, these two values can differ by 10-30 %. If FCR is calculated for economic purposes, the wasted feed must be included, as it causes costs and must be paid by the farmer. However, if FCR is calculated for scientific purposes (e.g., a performance trial), only the feed consumed should be included.
- Even if they are same-aged animals, individuals or groups differ in weight. Hence, they have different requirements for maintenance and also diverging quantity left for production. To avoid mistakes, weight-corrected FCR can be used.
- Nutrient utilization also depends on genotype and sex; thus, comparisons should consider these factors as they also influence weight gain and body composition (Patience et al., 2015).
Many factors influence the FCR
There are internal and external factors that influence feed efficiency. Internal factors originate in the animal and include genetics, age, body composition, and health status. In contrast, external factors include feed composition, processing, and quality, as well as the environment, welfare enrichment, and social aspects.
1. Species
Different species have different body sizes and physiology and, therefore, vary in their growth and maintenance requirements, impacting their efficiency in converting the feed.
Table 1: FCRs of different species
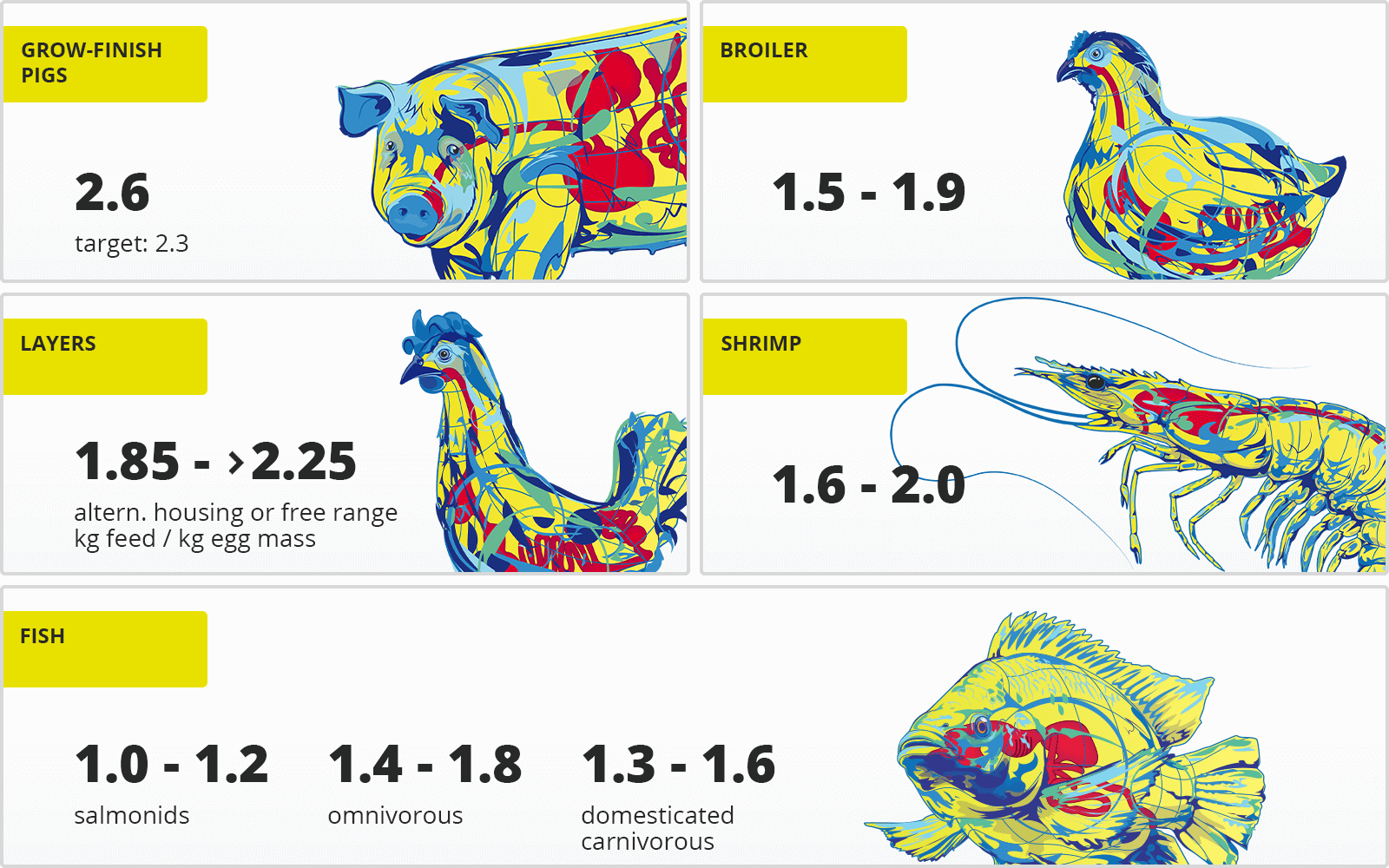
Compared to terrestrial animals, for example, fish and other aquatic animals have a low FCR. Being poikilothermic (animals whose body temperature ranges widely), they don’t spend energy on maintaining their body temperature if the surrounding water is within their optimal range. As they are physically supported by water, they also need less energy to work against gravity. Furthermore, carnivorous fish are offered highly digestible, nutrient-dense feed, which lowers their requirements in quantity. Omnivorous fish, on the other hand, also consume feedstuffs not provided by the producer (e.g., algae and krill), which is not considered in the calculation. Broilers are the only farm animals achieving a similar FCR.
2. Sex, age, and growth phase
Sex determines gene expression related to the regulation of feed intake and nutrient utilization. Males have a better feed conversion and put on more lean meat than females and castrates, which grow slower and easier run to fat.
Young animals have a fast growth rate and are offered nutritionally dense feed; hence, their FCR is lower. When the animal grows and gains weight, its energy requirement for maintenance increases and its growth rate and the feed nutrient density diminish.
Table 2: FCR during different life phases of pigs (based on Adam and Bütfering, 2009)
| Age / weight / phase | FCR | |
| Piglet | 0 – 2 weeks | 1.1 – 1.2 |
| 3 – 6 weeks | 1.6 – 1.8 | |
| Grower-finisher | 30 – 120 kg | ~ 2.6 |
| End of fattening | 4 – 5 |
3. Health and gut health
Health decisively impacts feed conversion. An animal that is challenged by pathogens reduces its feed intake and, thus, decreases growth. Additionally, the body needs energy for the immune defense, the replacement of damaged or lost tissue, and heat production, in case of fever. As many immune components are rich in protein, this is the first nutrient to become limited.
An imbalance in the gut microbiome also impacts feed conversion: pathogenic microorganisms damage tissues, impair nutrient digestion and absorption, and their metabolic products are harmful. Furthermore, pathogens consume nutrients intended for the host and continue to proliferate at its expense.
4. Environment
The environment influences the way the animals spend their maintenance energy. According to Patience (2012), when a 70 kg pig is offered feed ad libitum, 34 % of the daily energy is used for maintenance. For each °C below the thermoneutral zone, an additional 1.5% of feed is needed for maintenance. In heat stress, each °C above the optimum range decreases feed intake by 2%. Therefore, the feed needs to be denser to fulfill the requirement, or the animal will lose weight. Social stress also influences animal performance, especially chronic stress situations. Keeping the animals in their thermoneutral zone and mitigating the impact of stressors means more energy can go towards performance.
5. Feed quantity, composition, and quality
The feed is the source of nutrients animals convert into production. So, it’s natural that its quality and composition, and the availability of nutrients affect feed efficiency.
Better FCR by increasing nutrient density and digestibility
Higher energy content in the diet and better protein digestibility improve FCR. Saldaña et al. (2015) assert that increasing the energy content of a diet led to a linear decrease of the average daily feed intake but improved FCR quadratically. The energy intake by itself remained equal. However, these diet improvements also increase costs, and a cost-benefit analysis should be conducted.
Feed form and particle size play an important role
Feed processing can improve nutrient utilization. Particle size, moisture content, and whether the feed is offered as pellets or mash influence feed efficiency. Reducing the particle size leads to a higher contact surface for digestive enzymes and higher digestibility. Chewning et al. (2012) tested the effect of particle size and feed form on FCR in broilers. They found that pellet diets enable better FCRs than mash diets – one reason is the lower feed waste, another one the smaller feed particle size in the pelleted feed. Comparing the different tested mash diets, the birds receiving feed with a particle size of 300 µm performed better than the birds getting a diet with 600 µm particles.
Richert and DeRouchey (2015) show that pigs’ feed efficiency improved by 1.3 % for every 100 µm when the particle size was reduced from 1000 µm to 400 µm , as the contact surface for the digestible enzymes increased. In weaning piglets of 28-42 days, the increase of particle size from 394 µm to 695 µm worsened FCR from 1.213 to 1.245 (Almeida et al., 2020). There is a flipside to smaller particle size as well, however: high quantities of fines in the diet can lead to stomach ulceration in pigs (Vukmirović et al., 2021).
Non-starch polysaccharide (NSP)-rich cereals worsen FCR
The carbohydrates in feedstuffs such as wheat, rye, and barley are not only energy suppliers, and if not managed well, the inclusion of these raw materials can deteriorate feed conversion. Vegetable structural substances such as cellulose, hemicellulose, or lignin (e.g., in bran), are difficult or even impossible to utilize as they lack the necessary enzymes.
Figure 1: Contents of arabinoxylan and ß-glucan in grain (according to Bach Knudsen, 1997)
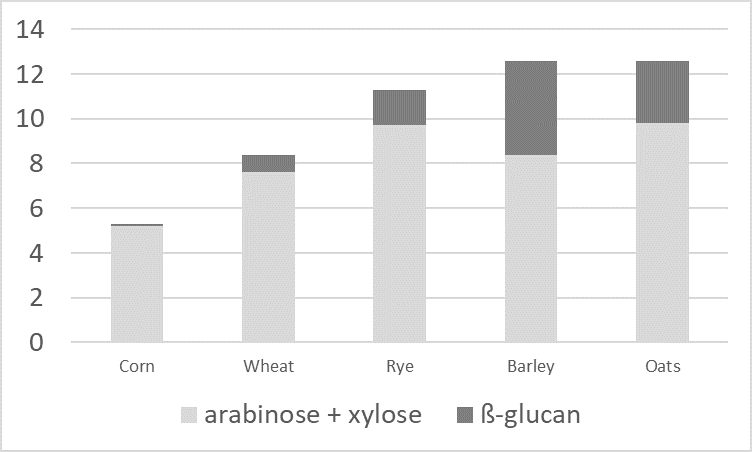
Additionally, water-soluble NSPs (e.g., pectins, but also ß-glucans and pentosans) have a high water absorption capacity. These gel-forming properties increase the viscosity of the digesta. High viscosity reduces the passage rate and makes it more difficult for digestive enzymes and bile acids to come into contact with the feed components. Also, nutrients’ contact with the resorptive surface is reduced.
Another disadvantage of NSPs is their “cage effect.” The water-insoluble NSPs cellulose and hemicellulose trap nutrients such as proteins and digestible carbohydrates. Consequently, again, digestive enzymes cannot reach them, and they are not available to the organism.
Molds and mycotoxins impair feed quality, but also animal health
Molds reduce the nutrient and energy content of the feed and negatively impact feed efficiency. They are dependent on active water in the feed and feed ingredients. Compared to bacteria, which need about 0.9-0.97 Aw (active water), most molds require only 0.86 Aw.
Table 3: Comparison of 28-day-old chicks performance fed not-infested and molded corn
| Weight gain (g) | FCR | |
| Non-infested corn | 767 a | 1.79 a |
| Molded corn | 713 b | 1.96 b |
Besides spoiling raw materials and feed and reducing their nutritional value, molds also produce mycotoxins which negatively impact animal health, including gut health. They damage the intestinal villi and tight junctions, reducing the surface for nutrient absorption. In a trial with broiler chickens, Kolawole et al. (2020) showed a strong positive correlation between the FCR and the exposure to different mycotoxins. The increase in levels of toxin mixtures resulted in poor FCR. Williams and Blaney (1994) found similar results with growing pigs. The animals received diets containing 50 % and 75 % of corn with 11.5 mg nivalenol and 3 mg zearalenone per kg. The inclusion of contaminated corn led to a deterioration of feed efficiency from 2.45 (control) to 3.49 and 3.23.
Oxidation of fats also affects feed quality
DDGS (distiller’s dried grains with solubles), by-products of corn distillation processes, are often used as animal feed, especially for pigs. The starch content is depleted in the distillation process and thus removed. The fat, however, is concentrated, and DDGS reach a similar energy content as corn.
Pigs also receive fats from different sources (e.g., soybean or corn oil, restaurant grease, animal-vegetable blends), especially in summer. Due to heat, the animals eat less, so increasing energy density in the feed is a possibility to maintain the energy intake. The high fat content, however, makes these feeds susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures.
The oxidation of feedstuffs manifests in the rancidity of fats, destruction of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, and E, carotenoids (pigments), and amino acids, leading to a lower nutritional value of the feed.
Use adequate supplements to enhance FCR
The feed industry offers many solutions to improve the FCR for different species. They usually target the animal’s digestive health or maintain/enhance feed quality, including increasing nutrient availability.
1. Boost your animals’ gut health
Producers can improve gut health by preventing the overgrowth of harmful microorganisms and by mitigating the effects of harmful substances. For this purpose, two kinds of feed additives are particularly suitable: phytomolecules and products mitigating the impact of toxins and mycotoxins.
Phytomolecules help stabilize the balance of the microbiome
By preventing the proliferation of pathogens, phytomolecules help the animal in three ways:
- They prevent pathogens from damaging the gut wall
- They deter and mitigate inflammation
- By inhibiting the overgrowth of pathogens, they promote better nutrient utilization by the animal
Only a healthy gut can optimally digest feed and absorb nutrients.
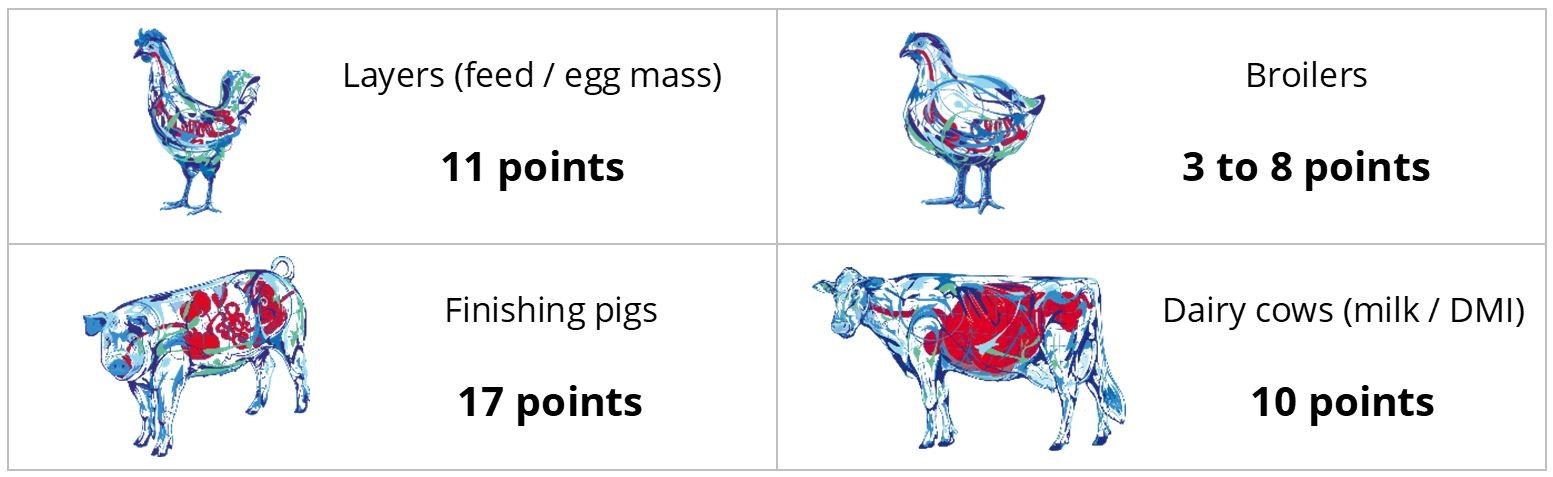
In trials testing the phytogenic Activo product range, supplemented animals showed the following FCR improvements compared to non-supplemented control groups (Figure 2). Note that phytomolecules also have a digestive effect that contributes to the FCR improvements:
Figure 2: FCR improvements for animals receiving Activo
Products mitigating the adverse effects of toxins
Both mycotoxins and bacterial toxins negatively impact gut health. Mycotoxins are ingested with the feed; bacterial toxins appear when certain bacteria proliferate in the gut, e.g., gram-negative bacteria releasing LPS or Clostridium perfringens producing NetB and Alpha-toxin.
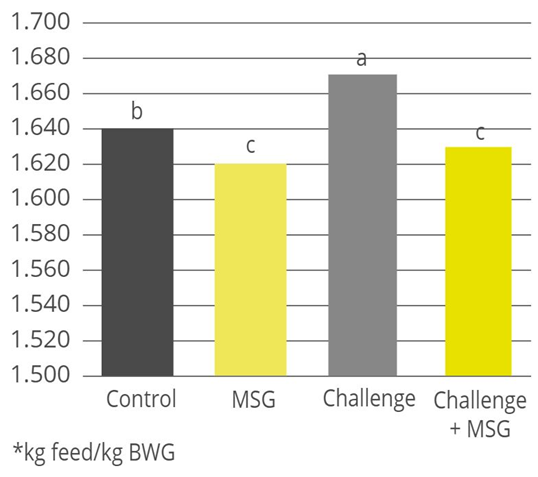
Products that mitigate the harmful effects of toxins help to protect gut health and maintain an optimal feed efficiency, as shown with a trial conducted with Mastersorb Gold:
Table 4: Trial design, the impact of Mastersorb Gold on broilers challenged with zearalenone and DON-contaminated feed
| Control | Mastersorb Gold | Challenge | Challenge + Mastersorb Gold | |
| Challenge | — | — | 300ppb zearalenone and 6000ppb DON | 300ppb zearalenone and 6000ppb DON |
| Additive | — | MSG (2 kg / MT of feed) | — | MSG (1 kg / MT of feed) |
Figure 3: Average FCR for broilers, with or without zearalenone and DON challenge, with or without Mastersorb Gold supplementation
2. Improve nutrient utilization
Maximum use of the nutrients contained in the feed can be obtained with the help of feed additives that promote digestion. Targeting the animal, selected phytomolecules are used for their digestive properties. Focusing on the feed, specific enzymes can unlock nutrients and thus improve feed efficiency.
Phytomolecules support the animal’s digestive system
Phytomolecules promote optimal digestion and absorption of nutrients by stimulating the secretion of digestive juices, such as saliva or bile, enhancing enzyme activity, and favoring good GIT motility (Platel and Srinivasan, 2004). FCR improvements thanks to the use of a phytomolecules-based product (Activo) are shown in figure 2.
Enzymes release more nutrients from feed
Enzymes can degrade arabinoxylans, for example. Arabinoxylans are the most common NSP fraction in all cereals – and are undigestible for monogastric animals. Enzymes can make these substances available for animals, allowing for complete nutrient utilization. Additionally, nutrients trapped due to the cage effect are released, altogether increasing the energy content of the diet and improving FCR.
3. Be proactive about preserving feed quality
The quality of feed can deteriorate, for instance, when nutrients oxidize, or mold infestation occurs. Oxidation by-products promote oxidative stress in the intestine and may lead to tissue damage. Molds, in turn, take advantage of the nutrients contained in the feed and produce mycotoxins. Both cases illustrate the importance of preventing feed quality issues. Feed additives such as antioxidants and mold inhibitors mitigate these risks.
Antioxidants prevent feed oxidation
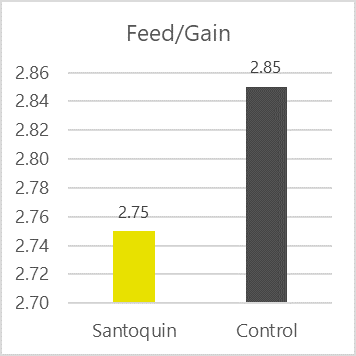
Antioxidants scavenge free radicals and protect the feed from spoilage. In animals, they mitigate the adverse effects of oxidative stress. Antioxidants in pig nutrition can stabilize DDGS and other fatty ingredients in the feed, maintaining nutrient integrity and availability. Figure 4 shows the FCR improvement that a producer in the US obtained when using the antioxidant product Santoquin in pork finisher diets containing 30% DDGS.
Figure 4: FCR improvement in pigs receiving Santoquin (trial with a Midwest pork producer)
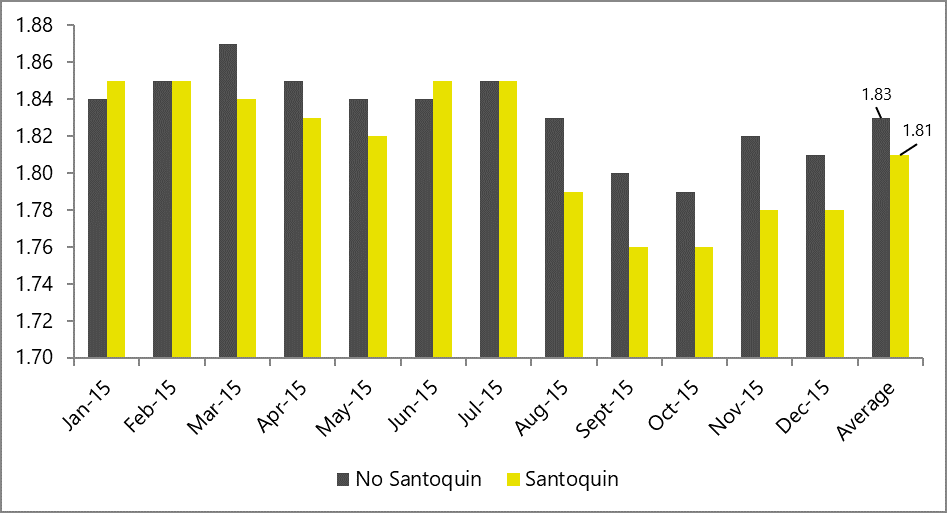
In DDGS-free diets, which are more common in poultry production, antioxidants also help optimize FCR, as shown by the results of a comprehensive broiler field study in 2015 (figure 5).
Figure 5: FCR in broilers receiving Santoquin, compared to a non-supplemented control group
Inhibiting molds and keeping feed moisture
To round off the topic of feed quality preservation, one should consider mold inhibitors, which also play an essential role. Used at the feed mill, these products blend two types of ingredients with their different modes of action: surfactants and organic acids. Surfactants bind active water so that the moisture of the feed persists, but fungi cannot survive. Organic acids, on the other hand, have anti-fungal properties, directly acting against molds. Both actions together prevent the reduction of energy in the feed, keeping feed efficiency at optimal levels.
Conclusion
The improvement of feed efficiency ranks as one of the most, if not the most, critical measures to cope with rising feed costs. By achieving optimal nutrient utilization, producers can make the most out of the available raw materials.
The feed industry offers diverse solutions to support animal producers in optimizing feed efficiency. Improving gut health, mitigating the negative impact of harmful substances, and maintaining feed quality are crucial steps to achieving the best possible FCR and, hence, cost-effective animal production.
References
Adam, F., and L. Bütfering. “Wann Müssen Meine Schweine an Den Haken?” top agrar. top agrar online, October 1, 2009. https://www.topagrar.com/schwein/aus-dem-heft/wann-muessen-meineschweine-an-den-haken-9685161.html.
Almeida, Leopoldo Malcorra, Vitor Augusto Zavelinski, Katiucia Cristine Sonálio, Kariny Fonseca da Silva, Keysuke Muramatsu, and Alex Maiorka. “Effect of Feed Particle Size in Pelleted Diets on Growth Performance and Digestibility of Weaning Piglets.” Livestock Science 244 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2020.104364.
Chewning, C.G., C.R. Stark, and J. Brake. “Effects of Particle Size and Feed Form on Broiler Performance.” Journal of Applied Poultry Research 21, no. 4 (2012): 830–37. https://doi.org/10.3382/japr.2012-00553.
Gaines, A. M., B. A. Peerson, and O. F. Mendoza. “Herd Management Factors That Influence Whole Feed Efficiency.” Essay. In Feed Efficiency in Swine, edited by J. Patience, 15–39. Wageningen Academic, 2012.
Kolawole, Oluwatobi, Abigail Graham, Caroline Donaldson, Bronagh Owens, Wilfred A. Abia, Julie Meneely, Michael J. Alcorn, Lisa Connolly, and Christopher T. Elliott. “Low Doses of Mycotoxin Mixtures below EU Regulatory Limits Can Negatively Affect the Performance of Broiler Chickens: A Longitudinal Study.” Toxins 12, no. 7 (2020): 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070433.
Patience, J. F. “The Influence of Dietary Energy on Feed Efficiency in Grow-Finish Swine.” Essay. In In Feed Efficiency in Swine, edited by J. Patience, 15–39. Wageningen Academic, 2012.
Patience, John F., Mariana C. Rossoni-Serão, and Néstor A. Gutiérrez. “A Review of Feed Efficiency in Swine: Biology and Application.” Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology 6, no. 1 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-015-0031-2.
Platel, K., and K. Srinivasan. “Digestive Stimulant Action of Spices: A Myth or Reality?” Indian J Med Res, pp 167-179 119 (May 2004): 167–79. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15218978
Richert, B. T., and J. M. DeRouchey. “Swine Feed Processing and Manufacturing.” Pork Information Gateway, September 14, 2015. https://porkgateway.org/resource/swine-feed-processing-and-manufacturing/.
Saldaña, B., P. Guzmán, L. Cámara, J. García, and G.G. Mateos. “Feed Form and Energy Concentration of the Diet Affect Growth Performance and Digestive Tract Traits of Brown-Egg Laying Pullets from Hatching to 17 Weeks of Age.” Poultry Science 94, no. 8 (2015): 1879–93. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pev145.
Vukmirović, Đuro, Radmilo Čolović, Slađana Rakita, Tea Brlek, Olivera Đuragić, and David Solà-Oriol. “Importance of Feed Structure (Particle Size) and Feed Form (Mash vs. Pellets) in Pig Nutrition – A Review.” Animal Feed Science and Technology 233 (2017): 133–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.06.016.
















